|
STATUS:
05.11.2020
Instrument Status:
The spacecraft continues to perform nominally.
SOFIE
SOFIE continues to collect nominal science observations, and housekeeping parameters all indicate a stable and healthy instrument. SOFIE V1.3 data are available online.
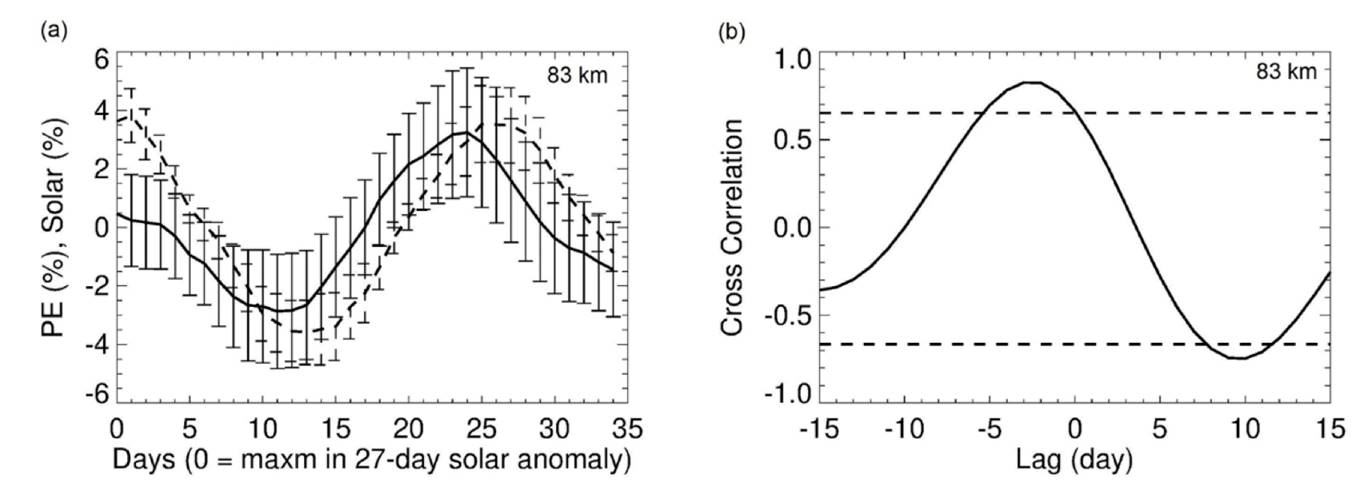
High-latitude summer mesospheric gravity wave (GW) activity was recently analyzed using nine years (2007-2015) of SOFIE and CIPS observations [Thurairajah et al., 2019]. GW activity is characterized in terms of potential energy per unit mass. SOFIE temperatures are used to derive daily averaged GW potential energy in the Northern Hemisphere summer, along with a new approach using CIPS PMC observations to derive temperature perturbations. July monthly averaged GW potential energy indicates no relationship to the 11-year solar cycle. Daily averaged values indicate a large seasonal variability in the 27-day GW oscillation, with positive, negative or no correlation with the 27-day solar rotation during individual summer seasons. A superposed epoch analysis using SOFIE GW anomalies, however, indicates a significant negative response to the 27-day solar signal with a lag of 8-12 days (See Figure below). We speculate that this 27-day GW response is linked to similar oscillations in the winds, but the exact cause of the 27-day signal in the GW activity is not understood.
Thurairajah, B., S. M. Bailey, M. E. Hervig (2019), Northern hemisphere summer mesospheric gravity wave response to solar activity from nine years of AIM observations, J. Atmos. Solar-Terr. Phys., https://doi.org/10.1016/ j.jastp.2019.105086. (article)
|
(a) SOFIE GW potential energy response (solid line) to solar forcing (dashed line) using superposed epoch analysis at 84 km. (b) Cross correlation between GW potential energy at 84 km and Lyman-alpha anomalies as a function of time lag. The horizontal dashed lines indicate the 90% confidence level. |
|
