|
STATUS:
08.28.2020
Instrument Status:
The spacecraft continues to perform nominally.
SOFIE
SOFIE
SOFIE continues to collect nominal science observations, and housekeeping parameters all indicate a stable and healthy instrument. SOFIE V1.3 data are available online.
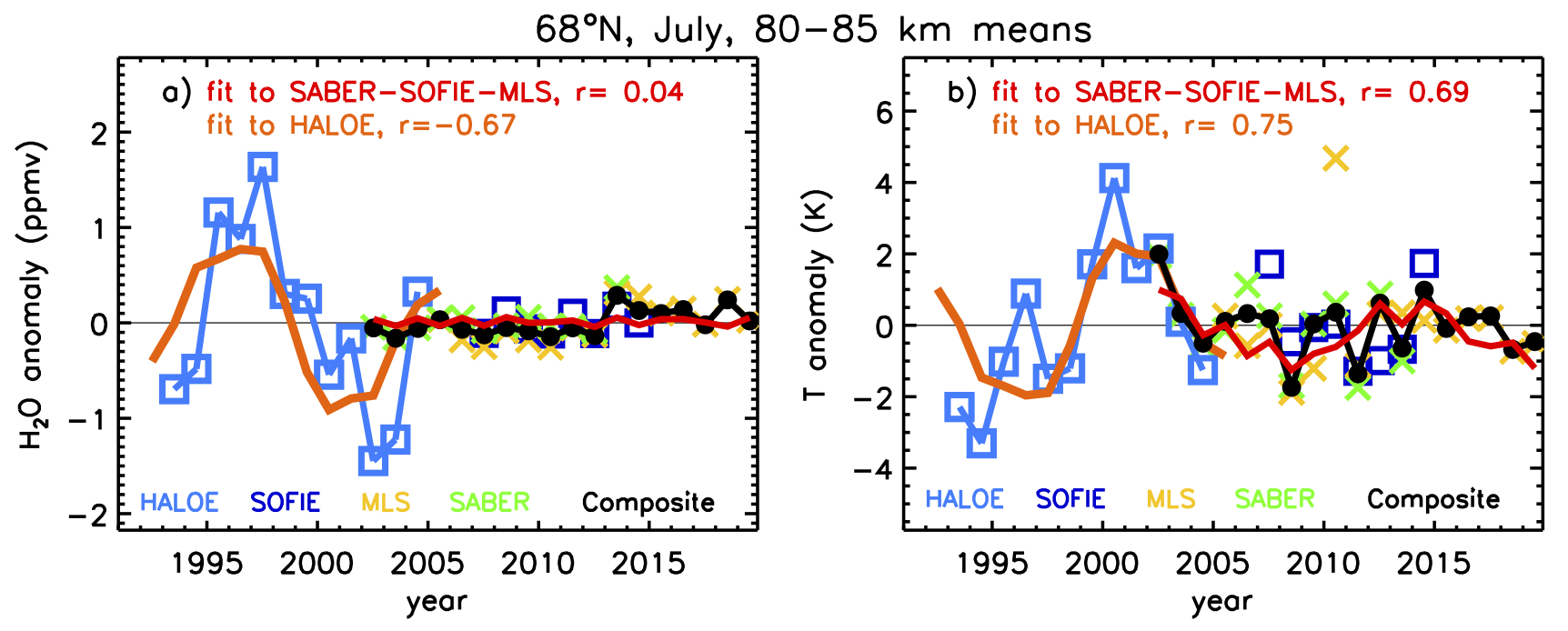
The response of the polar mesosphere to the 11-year solar cycle was recently investigated using satellite observations during 1979 - 2018, from SOFIE, CIPS, HALOE, SABER, MLS, and SBUV. Solar maximum is expected to cause higher temperatures and lower water vapor in the upper mesosphere, thus reducing the amount of ice in polar mesospheric clouds (PMC). While PMCs showed a clear anti-correlation with the solar cycle before roughly 2002, this response is absent during recent years. PMCs are controlled by temperature and water vapor, which were examined using mesospheric observations during 1992-2018. The main cause of the diminished solar cycle in PMCs near 68°S and 68°N appears to be a dramatic suppression of the solar cycle response of water vapor (see Figure). The solar cycle response of temperature also decreases after 2002, but calculations show that the decreased H2O response had more than three times the impact on PMCs than the reduction in temperature response.
Hervig, M. E., Siskind, D. E., Bailey, S. M., Merkel, A. W., DeLand, M. T., & Russell, J. M., III (2019), The missing solar cycle response of the polar summer mesosphere. Geophysical Research Letters, 46. https://doi.org/ 10.1029/2019GL083485. (article)
|
Time series of monthly mean H2O and temperature anomalies at 68°N in July, for 80 - 85 km averages. a) H2O measurements from HALOE and a composite of SOFIE, SABER, and MLS. b) Temperature measurements from HALOE and a composite of SABER, SOFIE, and MLS. Linear regression to solar Lyman-α is shown with regression coefficients (r) as listed. The 95% significance level was |r| > ~0.5. |
|
